Frontend Masters: Functional Javascript First Steps
References
- Observable HQ notebook: https://observablehq.com/collection/@anjana/functional-javascript-first-steps
- https://www.recurse.com
- https://codewords.recurse.com/issues/one/an-introduction-to-functional-programming
- Tail Call Optimisation: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-PX0BV9hGZY
- Map Reduce sandwich: https://www.datasciencecentral.com/forum/topics/what-is-map-reduce
What is Functional Programming
- A software programming paradigm
- imperative - do this, do that e.g. object oriented programming - keep state to yourself, send and receive messages
- declarative - this is what I want, do it however you want e.g. functional
- All boils down to the concept of pure functions
- only input in
- only output out
- no side effects allowed - no communication outside OTHER than via input or output
- A pure function is deterministic. The output is totally determined by its inputs.
- Functional programs are only concerned with the computational aspects. Parts with side effects e.g. logging, updates to databases etc are still required, but are “pushed to the outside” and kept separate from functional parts.
- Look at nothing but the input. Do nothing but return output
- Randomness is NOT deterministic, so not pure. Push to the outside of the program.
Staying out of the Loop with Recursion
- Iteration - imperative, looping, stateful e.g. loop variable which makes it hard to think about because we have to track these variables through the iterations and think what the value of it is now
- Recursion - functional, self-referential, stateless - goes better with functional programming
- Tail recursion - if written in the correct way, the code can be optimised by the JavaScript engine. “Proper tail calls” language feature added in ES6 which helps with this problem.
Higher Order Functions
Higher Order Function : Takes other functions as inputs and / or outputs
This is a key technique in functional programming. map, reduce, filter are all higher order functions.
Closure
When returning a function from another function, the function returned will still have access to any variables which were in scope when it was returned.
function makeAdjectifier(adjective) {
return function (noun) {
return adjective + " " + noun;
};
}
const coolify = makeAdjectifier("cool");
coolify("workshop"); // "cool workshop"
coolify("drink"); // "cool drink"Partial Application
Can therefore have functions which remember certain arguments “partially apply” to “lock in” some arguments and make more reusable functions.
Currying
Breaks up a multi argument function into a series of single arg ones. This makes it easier to reuse the smaller functions.
Function Composition
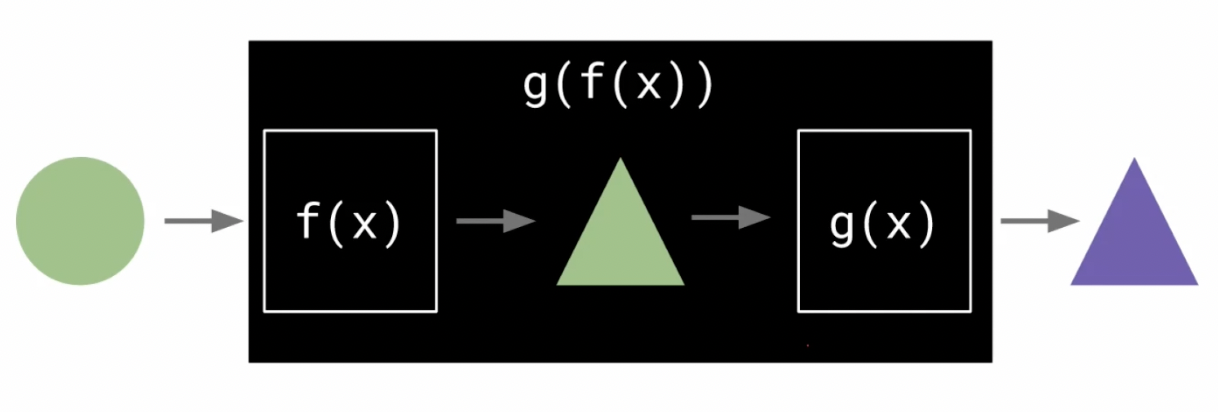
This is almost the opposite of currying. Having broken down functions into smaller one argument functions, we then construct programs entirely out of modular pure functions, using function composition to “combine” several functions’ effects to create a pipeline through which our program’s data can flow.
Immutability
Avoid mutability for happier programming. However copying data is not efficient. It takes time AND space. This is a challenge for functional programming.
The solution is special types of data structures which are immutable BUT also effecient. These are known as “immutable data structures” / “persistent data structures”
Immutable.js and Immer are two popular libraries.
Next Steps
Anouk Ruhaak
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6f5dt923FmQ
State has to deal with 3 issues:
- Race conditions - code which checks an external flag and then does something based on the value of the external flag will work great with 1 thread, but can suffer from race conditions for more than 1 thread:
IF no orange in the basket THEN get one and put it in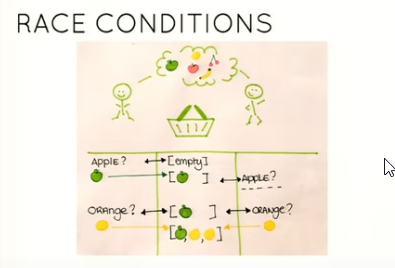
- Complexity - list, basket, but what about the type of supermarket, my mood for the day
- Unpredictability. Even a super simple function will return completely different things each time IF it depends on the value of an external variable
x = 1;
function timesTwo() {
return x * 2;
}
console.log(timesTwo(1)); // => 2
console.log(timesTwo(2)); // => 4Getting more relevant because today more and more code is run multi-threaded.
- ← Previous
Wes Bos: Flexbox - Next →
Schmidt-Jones: Understanding Basic Music Theory