Manning: Angular Development with TypeScript
Resources
- Source code: https://github.com/Farata/angulartypescript
- To Type or Not to Type: Quantifying Detectable Bugs in JavaScript: http://earlbarr.com/publications/typestudy.pdf
- Angular Material: https://material.angular.io
- Angular Material Guidelines: https://material.io/guidelines
- Webpack: http://webpack.js.org
- Event reference: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Events
Organisation
- Chapter 1: high level overview - cli - different ways to compile - intro to sample app ngAuction
- Chapter 2: components, ser- vices, directives, pipes and modules (page 44)
- Chapter 3: router (page 72)
- Chapter 4: advanced router - lazy loading modules (page 102)
- Chapter 5: dependency injection - providers and injectors - how to swap the object being injected (page 144)
- Chapter 6: observables -
switchMap(page 158) - Chapter 7: Flex Layout library -
ObservableMediaservice (page 176) - Chapter 8: loosely coupled intercomponent communication (page 203)
- Chapter 9: component lifecycle - change detection (page 232)
- Chapter 10: angular forms - template-driven and reactive (page 254)
- Chapter 11: Forms API - validators (page 275)
- Chapter 12: HTTP - HttpClient - also write web servers in Node and Express (page 302)
- Chapter 13: Sockets - push mechanism from server to client (page 335)
- Chapter 14: Testing (page 365)
- Chapter 15: Maintaining state in Redux style using NgRx (page 405)
- Appendix A: ECMAScript 6,7,8 language enhancements (page 428)
- Appendix B: TypeScript (page 463)
- Appendix C: npm and Yarn - semantic versioning (page 491)
- Appendix D: RxJS (page 498)
Chapter 1: Introducing Angular
The main advantage which React and Vue.js have over Angular is that they can be embedded easily within another web app. However this will be answered with the introduction of @angular/elements.
Angular Material is a library of approx 30 UI components. Further components are available in other 3rd party libraries e.g. PrimeNG, Kendo UI, DevExtreme. Can also use Bootstrap.
Introducing the Angular CLI
Assuming you have the latest version of the Angular CLI installed, running ng update will update all dependencies with package.json. See https://update.angular.io for further details on updating angular.
ng serve builds bundles in memory without creating files. The following files are generated (regenerated everytime a file changes):
inline.bundle.jsis a file used by the Webpack loader to load other filesmain.bundle.jsincludes your own code (components, services, and so on)polyfills.bundle.jsincludes polyfills needed by Angular so it can run in older browsersstyles.bundle.jsincludes CSS styles from your appvendor.bundle.jsincludes the code of the Angular framework and its dependencies
For each bundle, Angular CLI generates a source map file to allow debugging the original TypeScript, even though the browser will run the generated JavaScript. The size of the vendor.bundle.js in the dev build will be greatly reduced in the production build.
Angular CLI uses Webpack to build the bundles and webpack-dev-server to serve the app. ng serve runs webpack-dev-server. Starting Angular 7, Bazel is an alternative to Webpack.
JIT vs AOT compilation
Angular templates need to be compiled for the browser to understand them. With JIT, the compliation happens once the browser has downloaded all the files (the Angular compiler ngc is in the vendor.bundle.js).
Using JIT compilation in production is discouraged since the templates should be precompiled into JavaScript before the bundles are created (also save having to download the compiler). This is what ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation is about.
When bundles are built with the --prod option, Angular CLI performs code optimisation and AOT compilation. See it in action by running ng serve --prod. If third party libraries produce AOT errors, it can be turned off: ng serve --prod --aot false.
Whereas ng serve generates files in memory, the ng build command generates files in the dist directory (by default), but the bundle sizes won’t be optimized.
With ng build --prod, the generated files will be optimized but not compressed. Gzip compression will need to be applied afterwards.
Chapter 2: The main artefacts of an Angular app
Components
The main artefact - a class with a view (UI). To turn a class into a component, decorate it with the @Component() decorator. (These are Typescript decorators which are processed by the Angular compiler to add additional functionality. Similarity with @Input().)
- A component belongs to EXACTLY ONE module (declared in the
declarations) - Selectors for app projects start with
app-by default (lib-for libraries). It is good practice to come up with something unique for your application. Specify the prefix inangular.json
Services
Services are for code which fetches or manipulates data, for business logic.
- The
@Injectable()decorator ensures it is registered in the container - Use
provideIn: ``root``for Angular 6 upwards (previously had to declare in theproviderssection of (usually) the root module)
Directives
- Teach old HTML new tricks
- Two different types:
- structural which change the structure of a template e.g.
*ngForOR - attribute which change the behaviour or visual representation e.g.
ngModel
- structural which change the structure of a template e.g.
- Can also have custom directives
Pipes
A pipe | is a template element to transform output e.g. <p>Your birthday is {{ birthday | date }}</p>
- Various built in pipes e.g.
DatePipeand the name used on the template e.g.date - Others
| uppercase,| lowercase,| currency,| async(unwraps data from anObservablestream) - Some pipes take input parameters e.g.
| date:'medium' - Can chain pipes
- Can also have custom pipes
Modules
Container for a group of related components, services, directives and pipes e.g. for shipping or billing
- All apps must have at least one module - the root module - which is bootstrapped during application launch
- The root module must include the
BrowserModule, and contain thebootstrapconfiguration - Features modules must include the
CommonModuleinstead - Feature modules must
exportany components, services, classes, directives, pipes which need to be accessed by other modules
Data binding
Keeps a component’s properties in sync with the view
- Interpolation - simply use
{{ }}in the template e.g.<h1>Hello !</h1> - One-way binding class -> template: use
[]e.g.<span [hidden]="isValid">This field is required</span> - One-way binding template -> class: use
()e.g.<button (click)='getProducts()'>Get Products</button> - To gain access to the browser’s event object use
$evente.g.<button (click)='getProducts($event)'>Get Products</button>e.g. the target property specifies has the DOM element where the event occured - Can also have custom events (Chapter 8)
- Two-way binding invariably uses
ngModele.g.<input type='text' [(ngModel)]="shippingAddress">- if the value of the
shippingAddressvariable changes the value in the input field will be updated - if the value of the input field changes, the value of the
shippingAddressvariable will be updated
- if the value of the
- Remember to import the
FormsModuleforngModel
Chapter 3: Router basics
The <router-outlet> represents the content area used by the router - can have more than one (Chapter 4).
Configuration
- Two possible location strategies
HashLocationStrategy- works with all browsersPathLocationStrategy- aka History API based navigation - default - only works with browsers supporting HTML5- Uses the browser’s History API. This API allows programmatically going back and forth through the history stack as well as altering it
- For non root paths, requires a
<base href="/mypath">for the browser to resolve CSS etc and a value forAPP_BASE_HREFin the root module for Angular router to resolverouterLinkproperties and calls torouter.navigate()
- Configure routes by defining an array of type
Route(with the array of typeRoutes)
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: '', component: HomeComponent },
{ path: 'product', component: ProductDetailComponent }
];
- Routing is module based
- If declaring for the root module use
RouterModule.forRoot(routes)in theimportssection (the CLI’s--routingoption actually configures a seperate fileapp-routing.module.tsfor route configuration) forRootcreates a router module AND a serviceforChild(used in feature modules) only creates a router module
Navigation
- Navigation using
routerLink:<a [routerLink]="['/product']">Product Details</a> - Navigation using
navigate():this.router.navigate(['/product']) - By default the URL in the browser changes, but can be skipped using
skipLocationChange - Useful to create a 404 component and configure the route
**to display this component (catch all) e.g.{ path: '**', component: _404Component }
Passing data to routes
- Configure the route to include parameters e.g.
{ path: 'product/:id', component: ProductDetailComponent } - Pass the value in the routerLink:
<a [routerLink]="['/product', productId]">Product Detail</a> - The receiving component can get data from the route by injecting
ActivatedRoute - Access the
idusingroute.snapshot.paramMap.get('id') - CAREFUL using snapshot - it won’t change in some cases - need to subscribe to the
ActivatedRoute.paramMapproperty to get URL changes- e.g.
route.paramMap.subscribe( params => this.productID = params.get('id') );
- e.g.
Passing query parameters to routes
- Query parameters aren’t scoped to any particular route (so not specified in the route config)
- Using routerLink:
<a [routerLink]="['/products']" [queryParams]="{category:'sports'}">Sports products </a> - Using navigation requires access to the
Routerobject:this.router.navigate(['/products'], {queryParams: {category: 'sports'}}); - The receiving component can get query param data using
ActivatedRouteagain:route.snapshot.queryParamMap.get('category')
Child routes
The children property of Route is used to specify relative routes for child components e.g.
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: '', component: HomeComponent },
{ path: 'product/:id', component: ProductDetailComponent,
children: [
{ path: '', component: ProductDescriptionComponent },
{ path: 'seller/:id', component: SellerInfoComponent }
]
}
];
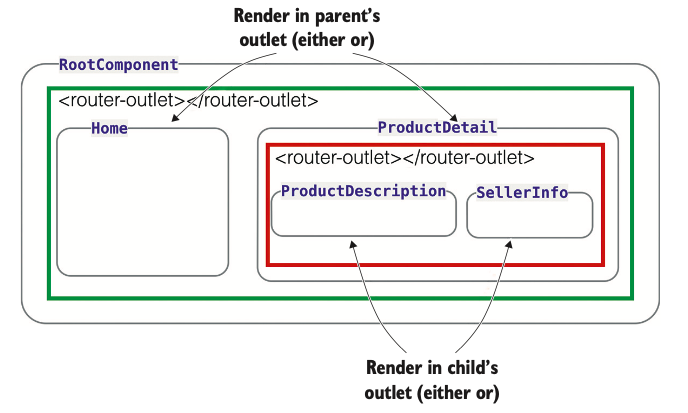
In this example, there are two <router-outlet>s:
- In the
app.component.html - In the
product.detail.component.html
:host
:host is a psuedo class selector which can be used with elements created using Shadow DOM (provides better encapsulation for components). Use :host to apply a background colour to the whole component e.g. :host { background: yellow; }
Deep linking
Although the link http://localhost:4200/#/product/1234/seller/5678 works when Angular’s index.html is loaded, it results in a 404 when it isn’t loaded. Any 404s should redirect to index.html so that “deep links” continue to work properly (Angular CLI dev server is already configured to do this).
Router events
There are various events which can be hooked into e.g. NavigationStart and NavigationEnd (see 6.6). For debugging, router events can be logged to the console via the forRoot() method: RouterModule.forRoot(routes, { enableTracing: true })
Chapter 4: Router advanced
Chapter 5: Dependency injection in Angular
Using Angular Material Components
- Angular Material is a library offering 30 UI Components and 4 prebuilt themes.
- A theme is a collection of palettes which look good together. 500 is the primary colour for the palette
- A prebuilt theme file can be reference in the
index.htmlOR the globalstyles.cssat e.g.@angular/material/prebuilt-themes/indigo-pink.css - Reference colours using e.g.
primary,accent,warnetc e.g.<mat-toolbar color="primary"></mat-toolbar> - Each of the 30 components is packaged in a feature module, so any used need to be imported in either
AppModuleOR in can be added to a seperate feature module e.g.MyAppMaterialModuleto retain separation (import this module into theAppModule). Only add those modules required.
Adding MAT to an Angular app
- Install libraries manually using:
npm i @angular/material @angular/cdk @angular/animations - Alternatively
npm add @angular/materialadds libraries and also updates source files as required (for details see: https://material.angular.io/guide/getting-started)
Chapter 7: Laying out pages with Flex Layout
- The term Responsive Web Design (RWD) was coined by Ethan Marcotte in the article “Responsive Web Design,” available at http://alistapart.com/article/responsive-web- design
- The Flex Layout Library in combination with its
ObservableMediaservice allows writing responsive designs with minimal CSS. - Write RWDs with:
- CSS
@mediaqueries and breakpoints - CSS Flexbox with
@mediaqueries - LINK - CSS Grid - LINK
- Angular Flex Layout library - doesn’t require CSS with
@mediaqueries. Instead uses directives. Full documentation at: https://github.com/angular/flex-layout/wiki. PURE TYPESCRIPT LAYOUT ENGINE.
- CSS
Using Flex Layout directives
- Two types of directives: one for containers and one for children:
- container directives for aligning children
- children directives for order, space taken etc
Directive | Description | Values
–|–
Container directives
fxLayout | Use CSS Flexbox to layout children | row, column, row-reverse, column-reverse
fxLayout.sm | Specify layout for particular sizes only | Also fxLayout.lt-md for e.g. all breakpoints less than medium
fxLayoutAlign | Specify alignment for child elements | either main-axis or cross-axis; start, center, end
fxLayoutGap | Controls space between child elements | %, px etc
Child directives
fxFlex | Controls the amount of space a child takes | %, px, grow, shrink, basis
fxFlexAlign | Change the alignment specified with fxLayoutAlign | start, baseline, center, end
fxFlexOrder | Change order of elements e.g. move an important component to visible area on smaller screens
- Add Flex Layout library:
npm i @angular/flex-layout @angular/cdk - Import the
FlexLayoutModulein the root module
MediaObserver service
Subscribe to screen size changes using the MediaObserver service’s media$ observable
export class AppComponent {
showExtras$: Observable<boolean>;
constructor(private mediaObserver: MediaObserver) {
this.showExtras$ = mediaObserver.media$
.pipe(map(change => {
return change.mqAlias === 'md' ? true : false;
}));
}
Instead of checking the value of mqAlias every time it changes, can instead use isActive API to check if a particular breakpoint is currently active. Ensure the mediaObserver reference is public so that it is accessible in the template. Then simply use e.g. *ngIf="mediaObserver.isActive('md')"
SCSS syntax
- Variables - start with
$e.g.$font-stack: Helvetica, sans-serif;and can be used in CSS e.g.body {font: 100% $font-stack;} - Nesting - easier to read syntax for nested CSS selectors
- Mixins - allow defining blocks of styles e.g.
@mixin reset-list { margin: 0; padding: 0; list-style: none; }. These are used in other styles with@includee.g.ul { @include: reset-list; color: red; }. Can also define variables on a mixin. - Partials - files to be imported into other files. Name starts with
_e.g._theme.scss. Import using@importe.g.@import './theme';
Theming
- https://www.materialpalette.com - MAT theme colours
- Create _theme.scss - to import a theme from MAT
- In styles.scss
Chapter 14: Testing Angular applications
A unit test should verify that a known, fixed input produces a known, fixed output (Google engineer Elliotte Rusty Harold)
Jasmine is the recommended framework for writing unit tests for Angular applications (there are others). Jasmine comes with its own browser based test runner. Karma is an alternative command line based runner (easier to automate).
Unit test specs are writting BDD style e.g. StarsComponent emits the change rating event (and serves as program documentation). Assertions are followed by matchers e.g. expect(2 + 2).toEqual(4) OR expect(2 + 2).not.toEqual(5). Complete list of matchers are in @types/jasmine/index.d.ts
describe('MyCalculator', () => { // A suite description and a function implementing the suite
it('should know how to multiply', () => {
// The code that tests multiplication goes here
});
it('should not divide by zero', () => { // A spec to test division
// The code that tests division by zero goes here
}); });
Appendix A: An overview of ECMAScript
Appendix assumes familiarity with ES5, and only covers enhancements introduced for ES6, 7 and 8.
A2 Scope of variables
Scoping of var is confusing with the variable declaration hoisted to the top of the execution context e.g. function. Use of this is also not straightforward. ES6 solves these problems with the let and const keywords.
- All variable declarations using
varare hoisted to the top of their execution context (which is e.g. the function - note NOT the block). However variable initializations are not hoisted, so the variable is created with a value ofundefinedand if used before the initialization may cause issues - Use
letandconstto avoid this and use block scoping and non-hoisted variables
A3 Template literals and multiline strings
- e.g.
`Hello ${customerName}` - e.g.
`This string
runs over two lines with a carriage return in the middle`
A4 Optional parameters and default values
As per C#
A5 Arrow function expressions, this and that
let sum = (arg1, arg2) => arg1 + arg2;// no need for curly braces, no need to usereturn- multiline expressions require braces and
return const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; console.log( "Sum of elements is " + arr.reduce((a,b) => a+b));// prints 15console.log( "Even numbers are " + arr.filter( value => value % 2 === 0));// prints 2 4
Fat arrow functions ensure this behaves properly when you want to access this from a closure (callback function etc).
Reference: http://javascriptissexy.com/understand-javascripts-this-with-clarity-and-master-it/
-
All functions have properties (just as objects have properties)
-
When a function executes, it gets the
thisproperty—a variable with the value of *the object* that invokes the function where *this* is used- e.g.
person.fullName()-personis invoking the methodfullName() - e.g. JQuery
$("button").click(function(event) { console.log($(this).prop("name"))})- thebuttonis invoking the click event
- e.g.
- ← Previous
Haverbeke: Eloquent JavaScript - Next →
Redis Certified Developer Program